For orbital period generally we refer to the sidereal period, that is the temporal cycle that it takes an object to make a full orbit, relative to the stars. This is the orbital period in an inertial (non-rotating) frame of reference (365,25 days for the earth).
To calculate the orbital period of the planets it is sufficient to consider the Newton's laws. If a planet with mass Mp moves in circular motion around the Sun (Msun = 1.98855 × 1030 kg), then the net centripetal force acting upon this orbiting planet is given by
where ω=(2π/T) is the angular velocity of the planet, and r is the distance from the Sun.
This centripetal force is the result of the gravitational force that attracts the planet towards the Sun
where G=6.67408 × 10-11 m3 kg-1 s-2 is the universal gravitational constant.
Since Fgr = Fcen, thus
⇓
Note that the orbital period does not depend on the mass of the planet but only on its distance from the Sun.
Example - The distance Earth/Sun is rearth = 1.4960×1011 m, thus
The distance Mars/Sun is rmars = 2.2794×1011 m, thus
 |
| A simple way to remember (approximately) the orbital periods of the planets of the solar system. |

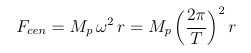






Comments
Post a Comment